- From: Dimitre Novatchev <dnovatchev@gmail.com>
- Date: Mon, 18 Mar 2024 14:44:27 -0700
- To: "Liam R. E. Quin" <liam@fromoldbooks.org>
- Cc: "public-xslt-40@w3.org" <public-xslt-40@w3.org>
- Message-ID: <CAK4KnZcvqEbi7aVh9MRK4-hy0Q2jRU+OdOJTD5BpnypRw5kHPA@mail.gmail.com>
> The best way right now to do a descending sort is sort() ! reverse().
> However, there’s no such easy way to do a descending sort keeping all
> the null values (or empty strings) at the end.
Thank you Liam, for the detailed explanation of the subtleties of some
collations.
Here is a complete implementation of descending sort (with *any* collation)
without having to reverse the normal sort.
Note that the code, without the map, is mere 19 well-formatted lines:
let $hexCodepoints := function($input as xs:hexBinary) as xs:integer*
{
let $hexchars := map{
"00": 0, "01": 1, "02": 2, "03": 3, "04": 4, "05": 5, "06": 6, "07": 7,
"08": 8, "09": 9, "0A": 10, "0B": 11, "0C": 12, "0D": 13, "0E": 14, "0F":
15,
"10": 16, "11": 17, "12": 18, "13": 19, "14": 20, "15": 21, "16": 22,
"17": 23, "18": 24, "19": 25, "1A": 26, "1B": 27, "1C": 28, "1D": 29, "1E":
30, "1F": 31,
"20": 32, "21": 33, "22": 34, "23": 35, "24": 36, "25": 37, "26": 38,
"27": 39, "28": 40, "29": 41, "2A": 42, "2B": 43, "2C": 44, "2D": 45, "2E":
46, "2F": 47,
"30": 48, "31": 49, "32": 50, "33": 51, "34": 52, "35": 53, "36": 54,
"37": 55, "38": 56, "39": 57, "3A": 58, "3B": 59, "3C": 60, "3D": 61, "3E":
62, "3F": 63,
"40": 64, "41": 65, "42": 66, "43": 67, "44": 68, "45": 69, "46": 70,
"47": 71, "48": 72, "49": 73, "4A": 74, "4B": 75, "4C": 76, "4D": 77, "4E":
78, "4F": 79,
"50": 80, "51": 81, "52": 82, "53": 83, "54": 84, "55": 85, "56": 86,
"57": 87, "58": 88, "59": 89, "5A": 90, "5B": 91, "5C": 92, "5D": 93, "5E":
94, "5F": 95,
"60": 96, "61": 97, "62": 98, "63": 99, "64": 100, "65": 101, "66":
102, "67": 103, "68": 104, "69": 105, "6A": 106, "6B": 107, "6C": 108,
"6D": 109, "6E": 110, "6F": 111,
"70": 112, "71": 113, "72": 114, "73": 115, "74": 116, "75": 117, "76":
118, "77": 119, "78": 120, "79": 121, "7A": 122, "7B": 123, "7C": 124,
"7D": 125, "7E": 126, "7F": 127,
"80": 128, "81": 129, "82": 130, "83": 131, "84": 132, "85": 133, "86":
134, "87": 135, "88": 136, "89": 137, "8A": 138, "8B": 139, "8C": 140,
"8D": 141, "8E": 142, "8F": 143,
"90": 144, "91": 145, "92": 146, "93": 147, "94": 148, "95": 149, "96":
150, "97": 151, "98": 152, "99": 153, "9A": 154, "9B": 155, "9C": 156,
"9D": 157, "9E": 158, "9F": 159,
"A0": 160, "A1": 161, "A2": 162, "A3": 163, "A4": 164, "A5": 165, "A6":
166, "A7": 167, "A8": 168, "A9": 169, "AA": 170, "AB": 171, "AC": 172,
"AD": 173, "AE": 174, "AF": 175,
"B0": 176, "B1": 177, "B2": 178, "B3": 179, "B4": 180, "B5": 181, "B6":
182, "B7": 183, "B8": 184, "B9": 185, "BA": 186, "BB": 187, "BC": 188,
"BD": 189, "BE": 190, "BF": 191,
"C0": 192, "C1": 193, "C2": 194, "C3": 195, "C4": 196, "C5": 197, "C6":
198, "C7": 199, "C8": 200, "C9": 201, "CA": 202, "CB": 203, "CC": 204,
"CD": 205, "CE": 206, "CF": 207,
"D0": 208, "D1": 209, "D2": 210, "D3": 211, "D4": 212, "D5": 213, "D6":
214, "D7": 215, "D8": 216, "D9": 217, "DA": 218, "DB": 219, "DC": 220,
"DD": 221, "DE": 222, "DF": 223,
"E0": 224, "E1": 225, "E2": 226, "E3": 227, "E4": 228, "E5": 229, "E6":
230, "E7": 231, "E8": 232, "E9": 233, "EA": 234, "EB": 235, "EC": 236,
"ED": 237, "EE": 238, "EF": 239,
"F0": 240, "F1": 241, "F2": 242, "F3": 243, "F4": 244, "F5": 245, "F6":
246, "F7": 247, "F8": 248, "F9": 249, "FA": 250, "FB": 251, "FC": 252,
"FD": 253, "FE": 254, "FF": 255 },
$strInput := xs:string($input)
return
(
for $i in 1 to xs:integer(string-length($strInput) div 2),
$j in 2 * $i -1
return $hexchars(substring($strInput, $j, 2))
)
},
$invertBase64Binary := function($input as xs:base64Binary) as xs:integer*
{
let $hexBin := xs:hexBinary($input),
$codePoints := $hexCodepoints($hexBin)
return
(
for $cp in $codePoints
return 255 - $cp,
260
)
}
return
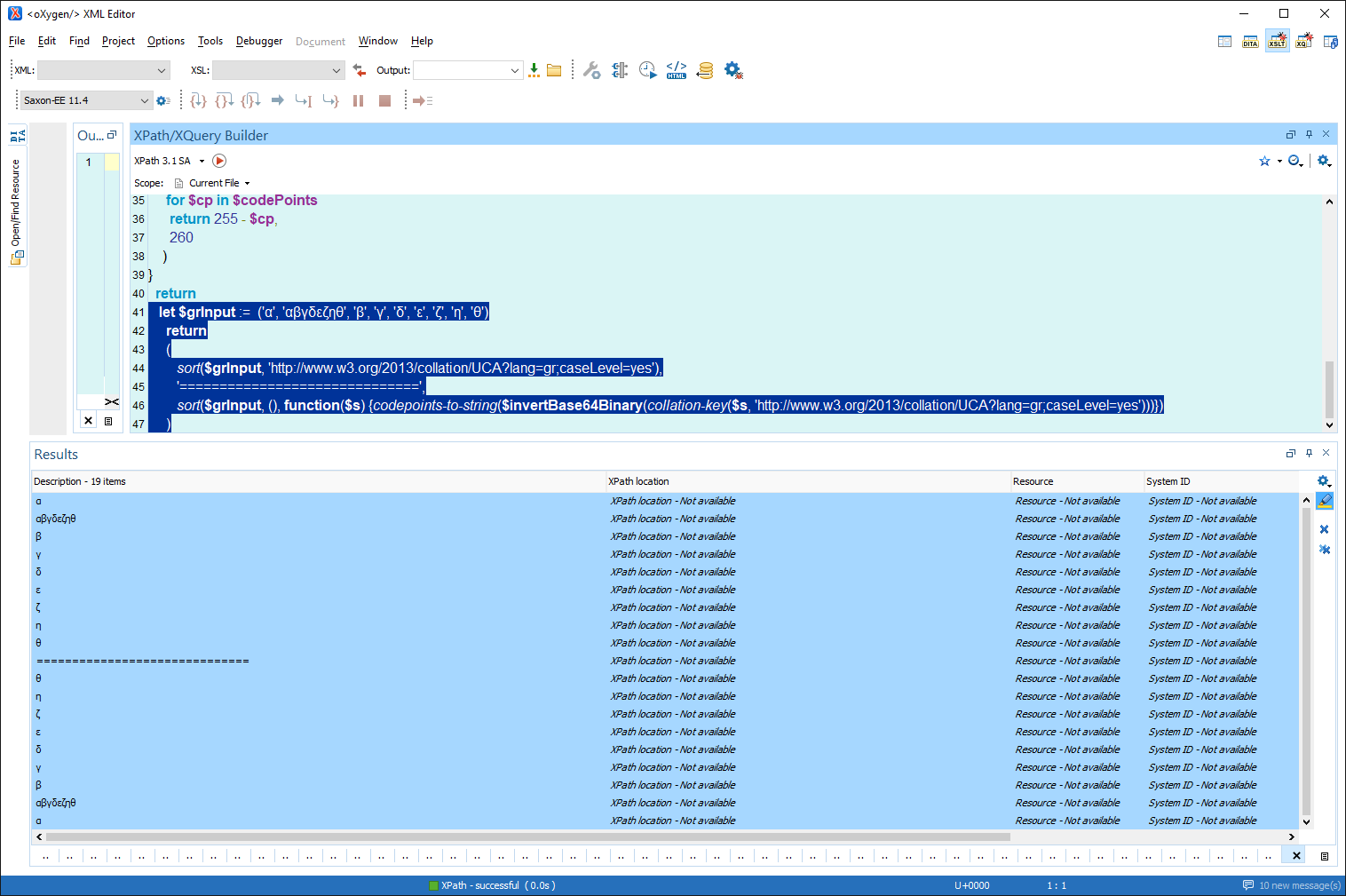
let $grInput := ('α', 'αβγδεζηθ', 'β', 'γ', 'δ', 'ε', 'ζ', 'η', 'θ')
return
(
sort($grInput, '
http://www.w3.org/2013/collation/UCA?lang=gr;caseLevel=yes'),
'==============================',
sort($grInput, (), function($s)
{codepoints-to-string($invertBase64Binary(collation-key($s, '
http://www.w3.org/2013/collation/UCA?lang=gr;caseLevel=yes')))})
)
=======================================================
I encourage everyone to try using the $invertBase64Binary function with
any collation they would like.
Here is the result of the above expression, that uses Greek strings, sorted
using the collation: "
http://www.w3.org/2013/collation/UCA?lang=gr;caseLevel=yes"
α
αβγδεζηθ
β
γ
δ
ε
ζ
η
θ
==============================
θ
η
ζ
ε
δ
γ
β
αβγδεζηθ
α
And a screenshot:
[image: image.png]
Having empty strings also produces the correct, expected results.
Many thanks to Michael Kay for pointing me to the *fn:collation--key*,
which plays a crucial part in this algorithm.
On Fri, Mar 15, 2024 at 2:34 PM Liam R. E. Quin <liam@fromoldbooks.org>
wrote:
> On Fri, 2024-03-15 at 13:26 -0700, Dimitre Novatchev wrote:
> >
> > SQL Server makes this as easy as:
> >
> > ```
> >
> > while (@codePoint < 255)
>
> Um, we have 21-bit codepoints, so we’d need 2097151.
> This isn’t practical.
>
> Yes, collations are chosen by “word of mouth” — actually by looking
> them up.
>
> In any event, knowing how a collation handles ch or æ or ß being sorted
> as ss, or combining diacriticals or ij or other multi-character
> combinations, comes from the reference documentation, not from
> inspecting a character at a time.
>
> We do include the HTML ascii-insensitive collation now in XPath, and
> that has case insensitivity for a-z/A-Z.
>
> In any case, e + combining-accent-grave had better sort the same as e-
> grave, and don't even think about character-at-a-time for Hindi.
> Spanish sorts S next to W. In Marathi (widely spoken in India) Lla (ळ,
> 933 sorts after Ha (ह, 939 and in Hindi it comes in codepoint order.
>
> Where multiple combining marks apply to a single base character (e.g.
> Hindi, Vietnamese, polytonic Greek), the input must be normalized by
> reordering as needed - see http://www.unicode.org/reports/tr15/
>
> The best way right now to do a descending sort is sort() ! reverse().
> However, there’s no such easy way to do a descending sort keeping all
> the null values (or empty strings) at the end.
>
> liam
>
> --
> Liam Quin, https://www.delightfulcomputing.com/
> Available for XML/Document/Information Architecture/XSLT/
> XSL/XQuery/Web/Text Processing/A11Y training, work & consulting.
> Barefoot Web-slave, antique illustrations: http://www.fromoldbooks.org
>
>
Attachments
- image/png attachment: image.png
Received on Monday, 18 March 2024 21:44:46 UTC