1 Introduction
SOAP Version 1.2 provides a request-response MEP and a response-only MEP. This, the SOAP One-way MEP, provides a one-way MEP.
1.1 Notational Conventions
The keywords "MUST", "MUST NOT", "REQUIRED", "SHALL", "SHALL NOT", "SHOULD", "SHOULD NOT", "RECOMMENDED", "MAY", and "OPTIONAL" in this document are to be interpreted as described in RFC 2119 [RFC 2119].
With the exception of examples and sections explicitly marked as "Non-Normative", all parts of this specification are normative.
2 SOAP One-way Message Exchange Pattern
This section defines the message exchange pattern (MEP) called "One-way". The description is an abstract presentation of the operation of this MEP. It is not intended to describe a real implementation or to suggest how a real implementation should be structured.
2.1 SOAP Feature Name
This message exchange pattern is identified by the URI (see SOAP 1.2 Part 1 [SOAP Part 1]SOAP Features):
"http://www.w3.org/2006/03/soap/mep/one-way/"
2.2 Description
The SOAP One-way MEP defines a pattern for the exchange of a SOAP message. In the absence of failure in the underlying protocol, this MEP consists of one SOAP message.
Abnormal operation during a one-way message exchange might be caused by a failure to transfer the message or a failure at the receiving SOAP node to process the message. Such failures might be silent at either or both of the sending and recieving SOAP nodes involved, or might result in the generation of a SOAP or binding-specific fault (see 2.4 Fault Handling). Also, during abnormal operation each SOAP node involved in the message exchange might differ in its determination of the successful completion of the message exchange.
The scope of a one-way MEP is limited to the exchange of a message between one sending and one receiving SOAP node. Implementations MAY choose to support multiple meps at the same time.
2.3 State Machine Description
The One-way MEP defines a set of properties described in ???.
| Property Name | Property Description | Property Type |
|---|---|---|
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/mep/OutboundMessage | An abstract structure that represents the current outbound message in the message exchange. This abstracts both SOAP Envelope and any other information structures that are transferred along with the envelope. | Not specified |
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/mep/InboundMessage | An abstract structure that represents the current inbound message in the message exchange. This abstracts both SOAP Envelope and any other information structures that are transferred along with the envelope. | Not specified |
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/mep/ImmediateDestination | The identifier of the immediate destination of an outbound message. | xs:anyURI |
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/mep/ImmediateSender | The identifier of the immediate sender of an inbound message. | xs:anyURI |
To initiate a message exchange conforming to the One-way MEP, the sending SOAP node instantiates a local message exchange context. ??? describes how the context is initialized.
| Property Name | Property Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/ExchangePatternName | "http://www.w3.org/2006/03/soap/mep/one-way/" | |
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/FailureReason | "None" |
A relative URI whose
base URI is the value of
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/ExchangePatternName |
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/Role | "SendingSOAPNode" |
A relative URI whose
base URI is the value of
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/ExchangePatternName |
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/State | "Init" |
A relative URI whose base URI is the value of
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/Role |
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/mep/OutboundMessage | An abstraction of the One-way message | |
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/mep/ImmediateDestination | An identifier (URI) that denotes the receiving SOAP node |
There may be other properties related to the operation of the message exchange context instance. Such properties are initialized according to their own feature specifications.
Once the message exchange context is initialized, control of the context is passed to a (conforming) local binding instance.
The diagram below shows the logical state transitions at
the sending and receiving SOAP nodes during the lifetime
of the message exchange. At each SOAP node, the local binding
instance updates (logically) the value of the
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/
ExchangeContext/State property to reflect the current
state of the message exchange. The state names are relative
URIs, relative to a base URI value carried in the
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/
ExchangeContext/Role property of the local message
exchange context.
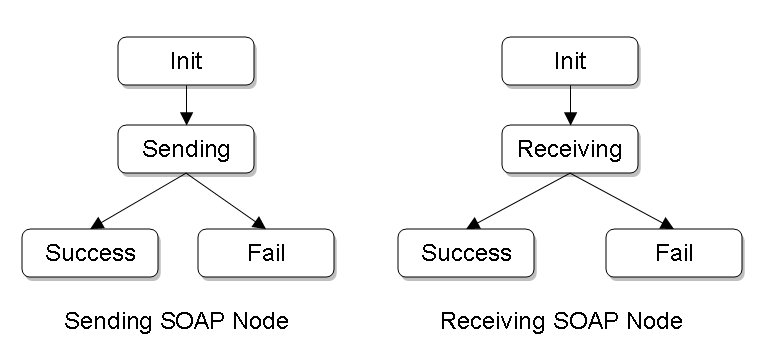
When the local binding instance at the receiving SOAP node starts to receive an inbound One-way message, it (logically) instantiates a message exchange context. ??? describes the properties that the binding initializes as part of the context's instantiation.
| Property Name | Property Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/ExchangePatternName | "http://www.w3.org/2006/03/soap/mep/one-way/" | Initialized as early as possible during the life cycle of the message exchange. |
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/FailureReason | "None" | A relative URI whose base URI is the value of http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/ExchangePatternName |
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/Role | "ReceivingSOAPNode" |
A relative URI whose base URI is the value of http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/ExchangePatternName
Initialized as early
as possible during the life cycle of the message
exchange.
|
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/State | "Init" | A relative URI whose base URI is the
value of http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/Role |
When the sending and receiving SOAP nodes transition between states, the local binding instance (logically) updates a number of properties. ??? and ??? describe these updates for the sending and the receiving SOAP nodes, respectively.
| CurrentState | Transition Condition | NextState | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| "Init" | Unconditional | "Sending" | Initiate transmission of message
abstracted in
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/mep/OutboundMessage. |
| "Sending" | Message transmission failure | "Fail" | Set
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/FailureReason to
"transmissionFailure" |
| Completed sending message. | "Success" |
| CurrentState | Transition Condition | NextState | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| "Init" | Start receiving message | "Receiving" | Set
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/mep/ImmediateSender to denote the sender of the message (if determinable).
Start making an abstraction of the message available in http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/mep/InboundMessage.
Pass control of message exchange context to SOAP processor. |
| "Receiving" | Message reception failure | "Fail" | Set
http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/FailureReason to
"receptionFailure". |
| Completed receiving message. | "Success" |
3 References
3.1 Normative References
- SOAP Part 2
- W3C Proposed Recommendation "SOAP Version 1.2 Part 2: Adjuncts", Martin Gudgin, Marc Hadley, Noah Mendelsohn, Jean-Jacques Moreau, Henrik Frystyk Nielsen, 24 June 2003 (See http://www.w3.org/TR/2003/REC-soap12-part2-20030624/.)
- RFC 2119
- IETF "RFC 2119: Key words for use in RFCs to Indicate Requirement Levels", S. Bradner, March 1997. (See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2119.txt.)
- RFC 2396
- IETF "RFC 2396: Uniform Resource Identifiers (URI): Generic Syntax", T. Berners-Lee, R. Fielding, L. Masinter, August 1998. (See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2396.txt.)
3.2 Informative References
- SOAP Part 0
- W3C Proposed Recommendation "SOAP Version 1.2 Part 0: Primer", Nilo Mitra, 24 June 2003 (See http://www.w3.org/TR/2003/REC-soap12-part0-20030624/.)
- SOAP Part 1
- W3C Proposed Recommendation "SOAP Version 1.2 Part 1: Messaging Framework", Martin Gudgin, Marc Hadley, Noah Mendelsohn, Jean-Jacques Moreau, Henrik Frystyk Nielsen, 24 June 2003 (See http://www.w3.org/TR/2003/REC-soap12-part1-20030624/.)
- XMLP Comments
- XML Protocol Comments Archive (See http://lists.w3.org/Archives/Public/xmlp-comments/.)
- XMLP Dist-App
- XML Protocol Discussion Archive (See http://lists.w3.org/Archives/Public/xml-dist-app/.)
- XMLP Charter
- XML Protocol Charter (See http://www.w3.org/2000/09/XML-Protocol-Charter.)
- RFC 2045
- IETF "RFC2045: Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) Part One: Format of Internet Message Bodies", N. Freed, N. Borenstein, November 1996. (See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2045.txt.)
- RFC 2026
- IETF "RFC 2026: The Internet Standards Process -- Revision 3", section 4.2.3, S. Bradner, October 1996. (See http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2026.txt.)