Status of this Document
This document is an editors' copy that has no official standing.
6. SOAP-Supplied Message Exchange Patterns
6.1 Property Conventions for MEPs
The following table describes the particular property definitions (in accordance with the property naming conventions defined in this document) which support the description of Message Exchange Patterns. Other properties may also be involved in the specification for particular MEPs, but these are generally applicable to all MEPs.
| Editorial note: JJM/JBI | 20020109 |
| The following table refers to PatternSpecificRole. This has not been defined previously. Should this be single:Role instead? | |
| Property Name | Property Description |
|---|---|
context:ExchangePatternName
|
A URI that names the message exchange pattern in operation. |
single:Role
|
A URI that names the pattern specific role of the local SOAP Node with respect to the message exchange denoted by the enclosing property container. |
single:State
|
A relative URI relative with a Base value carried in the PatternSpecificRole property which denotes the current state of the message exchange denoted by the enclosing property container. this value is managed by the binding instance and may be inspected by other entities monitoring the progress of the message exchange. |
context:FailureReason
|
A URI value that denotes a pattern specific, binding independent reason for the failure of a message exchange. Underlying protocol binding specifications may define properties to convey more binding specific details of the failure. |
context:OutboundMessage
|
An abstract structure that represents the current outbound message in a message exchange. This abstracts both SOAP Envelope and any other information structures that are transferred along with the envelope due to the action of the message exchange. |
context:InboundMessage
|
An abstract structure that represents the current inbound message in a message exchange. This abstracts both SOAP Envelope and any other information structures that are transferred along with the envelope due to the action of the message exchange. |
context:ImmediateDestination
|
A URI denoting the immediate destination of an outbound message. |
context:ImmediateSender
|
A URI denoting the immediate sender of an inbound message. |
6.2 Single-Request-Response MEP
This section defines the MEP "Single-Request-Response". The description is an abstract presentation of the operation of this MEP. It is not intended to describe a real implementation or to imply how a real implementation should be structured.
| Editorial note: HFN | 20020316 |
| Clarify 'single' in 6.1 as meaning pair with no temporal aspect. Avoid duplication with 6.1.3 | |
6.2.1 Message Exchange Pattern Name
This message exchange pattern is named by the URI "http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/mep/single-request-response/" abbreviated to "single-request-response" throughout this specification.
Underlying protocol binding specifications may use the full-name of this message exchange pattern to declare their support for the message exchange pattern and associated semantics described herein.
The following table lists the standard prefix mappings which we assume to hold throughout this section:
| Editorial note: HFN | 20020316 |
| For the record in the log, Noah suggests the editors give some additional thought to the prefix "single". I think something like ReqResp, or SingleReqResp, or even SReqResp would be a bit more suggestive of what's going on. | |
| Prefix | Namespace |
|---|---|
| context | "http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/" |
| mep | "http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/mep/" |
| fail | "http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/mep/FailureReasons/" |
| single | "http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/mep/single-request-response/" |
6.2.2 Informal Description
The single-request-response message exchange pattern defines a pattern for the exchange of two messages between two adjacent SOAP nodes along a SOAP Message Path. One message is exchanged in each direction between a Requesting SOAP Node and a Responding SOAP Node.
The normal operation of a message exchange conforming to the single-request-response exchange pattern is such that a Request Message is first transferred from Requesting SOAP Node to Responding SOAP Node. Following the successful processing of the Request Message by the Responding SOAP Node, a Response Message is then transferred from Responding SOAP Node to Requesting SOAP Node.
Abnormal operation of a message exchange conforming to the single-request-response exchange pattern may arise due to a failure to transfer the Request Message, a failure at the Responding SOAP Node to process the Request Message, or a failure to transfer the Response Message. Such failures MAY be silent at requesting, responding or both SOAP Node involved in the exchange. Also, under abnormal operation each SOAP Node involved in the message exchange MAY differ in their determination of the successful completion of the message exchange.
There is no implied timing relationship between contemporaneous exchanges conforming to this message exchange pattern, ie. nothing can be said about the relative temporal ordering of the transmission and reception of messages arising from distinct exchanges.
6.2.3 Formal Description
To initiate an message exchange conforming to the single-request-response message exchange pattern, the Requesting SOAP Node instantiates a local message exchange context. This context is initialised as follows:
| Property Name URI | Value |
|---|---|
context:ExchangePatternName
|
"http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/mep/single-request-response/" |
single:Role
|
RequestingSOAPNode |
single:State
|
Init |
context:FailureReason
|
None |
context:OutboundMessage
|
An abstraction of the Request Message |
context:ImmediateDestination
|
An identifier (URI) that denotes the Responding SOAP Node |
In addition other properties related to the operation of features to be used in conjunction with this particular instance of the message exchange are initialised in accordance with the relevant feature specification.
Once initialised control of the message exchange context is passed to a (conforming) local binding instance.
The diagram below shows the logical state transitions at requesting and responding SOAP Nodes during the lifetime of the message exchange. At each SOAP Node the value of the
single:State property is updated (logically) to reflect the current state of the message exchange as perceived by the local binding instance. These state names are relative URIs,
relative to a Base URI value carried in the single:Role property of the local message exchange context.
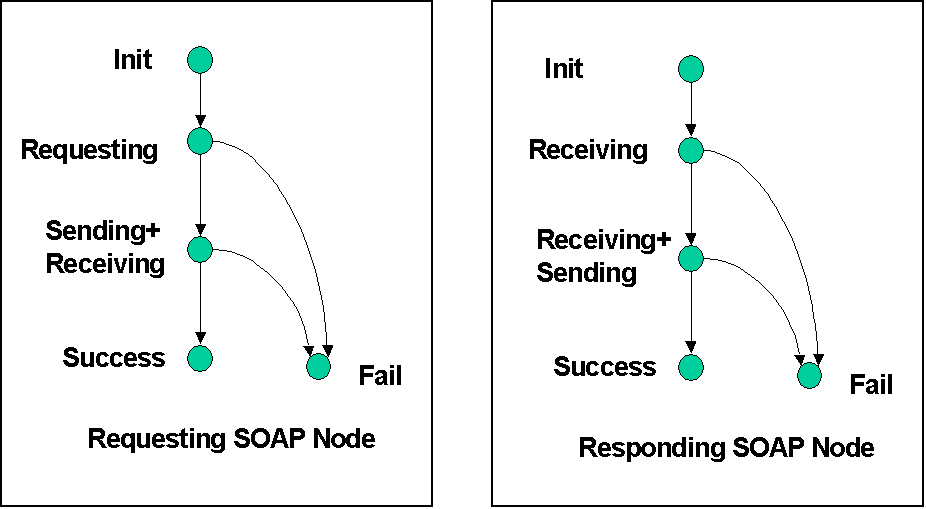
At the Responding SOAP Node a message exchange context is (logically) instantiated by the local binding instance when it starts to receive an inbound Request Message.
| Property Name | Value |
|---|---|
context:ExchangePatternName
|
"http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/mep/single-request-response/" Initialised as early as possible during the lifecycle of the message exchange. |
single:Role
|
RespondingSOAPNode Initialised as early as possible during the lifecycle the message exchange. |
single:State
|
Receiving |
context:FailureReason
|
None |
| Editorial note: JJM/TBTF - Awaiting final text from TBTF | 20020403 |
| Stuart has supplied text for this table***, although there was some further discussion amongst TBTF members. We are waiting for a final text from the TBTF. *** http://lists.w3.org/Archives/Member/w3c-xml-protocol-wg/2002Mar/0105.html | |
| CurrentState | Transition Condition | NextState | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Init | Unconditional | Requesting | Initiate transmission of Request Message abstracted in "context:OutboundMessage" |
| Requesting | Underlying protocol error | Fail | Set "context:FailureReason" to "transmissionFailure" |
| Local abort | Fail |
Set "context:FailureReason" to "localAbort"
Abort underlying protocol operation. |
|
| Start receiving Response Message |
Sending+ Receiving |
Set "context:ImmediateSender" to denote the sender of the Response Message (may differ from the value in "context:ImmediateDestination").
Start making an abstraction of the Response Message available in the "context:InboundMessage" |
|
|
Sending+ Receiving |
Underlying protocol error | Fail | Set "context:FailureReason" to "transmissionFailure" |
| Local abort | Fail |
Set "context:FailureReason" to "localAbort"
Abort underlying protocol operation. |
|
| Completed sending request message and Completed receiving response message | Success |
| CurrentState | Transition Condition | NextState | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Init | Start receiving Request Message | Receiving |
Set "context:ImmediateSender" to denote the sender of the Request Message (if determinable) Start making an abstraction of the Request Message available in "context:InboundMessage". Pass control of message exchange context to SOAP Processor. |
| Receiving | Underlying protocol error | Fail | Set "context:FailureReason" to "ReceptionFailure" |
| Local Abort | Fail |
Set "context:FailureReason" to "localAbort"
Abort underlying protocol operation. |
|
| Start of Response Message available in "context:OutBoundMessage" |
Receiving+ Sending |
Initiate transmission of Response Message abstracted in "context:OutBoundMessage". | |
|
Receiving+ Sending |
Underlying protocol error | Fail | Set "context:FailureReason" to "transmissionFailure". |
| Local Abort | Responding |
Set "context:FailureReason" to "localAbort"
Abort underlying protocol operation. |
|
| Completed receiving Request Message and Completed sending Response Message | Success |
6.2.4 Fault Handling
During the operation of the single-request-response message exchange pattern, the participating SOAP nodes may generate SOAP faults.
If a SOAP fault is generated by the Responding SOAP node while it is in the Processing state, the generated SOAP fault replaces the abstraction of the Response Message that is used to set the "context:OutboundMessage" property and the state machine transitions to the Responding state.
This MEP specification makes no claims as to the disposition or handling of SOAP faults generated by the Requesting SOAP node during the processing of the Response Message that follows the Success state in the Requesting SOAP node's state transition table.
7. SOAP HTTP Binding
7.1 Introduction
The SOAP HTTP Binding presented here provides a binding of SOAP to HTTP. This binding conforms to the SOAP Binding Framework (see [SOAP-PART1]SOAP Protocol Binding Framework) and uses abstract properties as a descriptive tool for defining the functionality of certain features.
The SOAP Protocol Binding Framework (see [SOAP-PART1]SOAP Protocol Binding Framework), Message Exchange Pattern Specifications (see ) and Feature Specifications (see 5. A Convention for Describing Features and Bindings) each describe the properties they expect to be present in a message exchange context when control of that context passes between the local SOAP Node and a binding instance.
Properties are named with XML qualified names (QNames). Property values are determined by the Schema type of the property, as defined in the specification which introduces the property. The following table lists the XML namespace prefix mappings that are used throughout this specification:
| Prefix | Namespace |
|---|---|
| context | "http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/bindingFramework/ExchangeContext/" |
| mep | "http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/mep/" |
| fail | "http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/mep/FailureReasons/" |
| single | "http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/mep/single-request-response/" |
HTTP applications MUST use the media type "application/soap+xml" according to [soap-media-type] when including SOAP 1.2 messages in HTTP exchanges. See [soap-media-type] for parameters defined by this media type and their recommended use.
Note:
Use of the SOAP HTTP Binding is optional; nothing precludes the specification of different bindings to other protocols or other bindings to HTTP. Because of the optionality of using the SOAP HTTP Binding, it is NOT a requirement to implement it as part of a SOAP node. A node that does correctly and completely implement the HTTP binding may to be said to "conform to the SOAP 1.2 HTTP binding."
7.2 Binding Name
The binding described here is identified with the URI:
-
"http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/bindings/HTTP/"
7.3 Supported Message Exchange Patterns
An implementation of the SOAP HTTP Binding MUST support the following message exchange pattern:
-
"http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/mep/single-request-response/" (see 6.2 Single-Request-Response MEP)
7.4 Single-Request-Reponse Message Exchange Operation
The "http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/mep/single-request-response/" message exchange pattern is described in 6.2 Single-Request-Response MEP.
For binding instances conforming to this specification:
-
A SOAP Node instantiated at an HTTP client may assume the role (i.e. the property
single:Role) ofRequestingSOAPNode. -
A SOAP Node instantiated at an HTTP server may assume the role (ie. the property
single:Role) ofRespondingSOAPNode.
The remainder of this section describes the MEP state machine and its particular relation to the HTTP protocol. In the state tables below, the states are defined as values for the
property single:State (see 6.2 Single-Request-Response MEP), and are of type
single:StateType (an enumeration over xs:string ).
Failure reasons as specified in the tables represent values of the property context:FailureReason - their values are QNames. If an implementation enters the "Fail" state, the
context:FailureReason property will contain the value specified for the particular transition.
7.4.1 Behaviour of Requesting SOAP Node
The overall flow of the behaviour of a Requesting SOAP Node follows the outline state machine description contained in 6.2 Single-Request-Response MEP. The following subsections describe each state in more detail.
7.4.1.1 Init
| Statename | Init | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Formulate and start sending HTTP Request (see table below) | ||
| Preconditions | See 6.2.3 Formal Description | ||
| Postconditions | None | ||
| Transitions | Event/Condition | NextState | Failure Reason |
| Unconditional | Requesting | N/A | |
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| HTTP Method | POST (the use of other HTTP methods is currently undefined in this binding). |
| Request URI |
The value of the URI carried in the context:ImmediateDestination property of the message exchange context.
|
| Content-Type header | "application/soap+xml" (see 7.1 Introduction) |
| Additional Headers |
Generated in accordance with the rules for the binding specific expression of any optional features in use for this message exchange e.g. SOAPAction (see 7.5.1 SOAP Action).
|
| HTTP entity body |
XML 1.0 serialisation of the SOAP message XML Infoset carried in the context:OutboundMessage property of the message exchange context. This binding mandates support
for UTF-8 and UTF-16.
|
7.4.1.2 Requesting
| Statename | Waiting | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Sending Request Message and waiting for the start of a Response Message, a protocol failure or a local abort. | ||
| Preconditions | None | ||
| Postconditions |
|
||
| Transitions | Event/Condition | NextState | Failure Reason |
| HTTP Response Status Line and HTTP Headers received | (see status code table below) | (see status code table below) | |
| Underlying protocol error | Fail |
fail:transmissionFailure
|
|
| Local Abort | Fail |
fail:localAbort
|
|
The following table details the HTTP status code dependent transitions upon reception of an HTTP status line and response headers.
| Status Code | Reason phrase | Significance/Action | NextState | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2xx | Successful | |||
| 200 | OK |
The Response Message follows in HTTP response entity body. Start making an abstraction of the Response Message available in "context:InboundMessage". |
Sending+ Receiving |
|
| 202 | Accepted |
The Request Message has been received and processed. The entity body of the HTTP response MAY contain a Response Message. Start making an abstraction of the Response Message available in "context:InboundMessage". |
Sending+ Receiving |
|
| 204 | No Content |
The Request message has been received and processed. The HTTP response MUST NOT contain an entity body. The message exchange is regarded as having completed successfully. |
Sending+ Receiving |
|
| Instantiated Property | Value | |||
context:CurrentMessage
|
"Empty" SOAP Envelope. | |||
| 3xx | Redirection |
The requested resource has moved and the HTTP request SHOULD be retried using the URI carried in the associated Location header as the new value for the |
Init (Optional?) |
|
| 4xx | Client Error | |||
| 400 | Bad Request |
Indicates a problem with the received HTTP Request Message. This may include a malformed XML in the Request-Message envelope. This operation SHOULD NOT be repeated with the same message content. The message exchange is regarded has having completed unsuccessfully. |
Fail | |
| Instantiated Property | Value | |||
context:FailureReason
|
fail:BadRequest
|
|||
| 401 | Unauthorized |
Indicates that the HTTP Request requires authorization. |
Fail | |
| Instantiated Property | Value | |||
context:FailureReason
|
fail:AuthenticationFailure
|
|||
| If the simple authentication feature is unavailable or the operation of simple authentication ultimately fails, then the message exchange is regarded as having completed unsuccessfully. |
Fail |
|||
| Instantiated Property | Value | |||
context:FailureReason
|
fail:AuthenticationFailure
|
|||
| 405 | Method not allowed |
Indicates that the peer HTTP server does not support the requested HTTP method at the given request URI. The message exchange is regarded has having completed unsuccessfully. |
Fail | |
| Instantiated Property | Value | |||
context:FailureReason
|
fail:BindingMismatch
|
|||
| 415 | Unsupported Media Type |
Indicates that the peer HTTP server does not support Content-type used to encode the Request Message. The message exchange is regarded has having completed unsuccessfully. |
Fail | |
| Instantiated Property | Value | |||
context:FailureReason
|
fail:BindingMismatch
|
|||
| 427 | SOAPAction Required |
Indicates that the peer HTTP server implements the OPTIONAL SOAPAction feature and that it requires that this node provide a SOAPAction header when resubmitting a similar HTTP request. The message exchange is regarded has having completed unsuccessfully. In requesting SOAP nodes that support the OPTIONAL SOAPAction feature, the behaviour described in 7.5.1 SOAP Action is applied. |
Fail | |
| 5xx | Server Error | |||
| 500 | Internal Server Error |
Indicates that the Response Message contained in the following HTTP response entity body may contain an SOAP fault. Other internal server errors may be the cause of this status code. The local binding instance continues to receive the incoming message. Start making an abstraction of the Response Message available in "context:InboundMessage". |
Sending+ Receiving |
|
| Instantiated Property | Value | |||
context:FaultHint
|
true | |||
Note:
There may be elements in the HTTP infrastructure configured to modify HTTP response entity bodies for 4xx and 5xx status code responses; for example, some existing HTTP origin servers have such a feature as a configuration option. This behavior may interfere with the use of 4xx and 5xx status code responses carrying SOAP fault messages in HTTP. It is recommended that such behavior is disabled for resources accepting SOAP/HTTP requests. If the rewriting behavior cannot be disabled, SOAP/HTTP cannot be used in such configurations.
7.4.1.3 Sending+Receiving
| Statename | Sending+Receiving | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Completing the transmission of a Request Message and the Reception of a Response Message. | ||
| Preconditions | None | ||
| Postconditions |
On transitions to Success: property context:InboundMessage contains an Infoset representation of the serialized envelope in the response body.
|
||
| Transitions | Event/Condition | NextState | Failure Reason |
| Request Message Transmission and Response Message Reception completed and a Well formed Response Message Received | Success | N/A | |
| Reception Failure (broken connections etc.) | Fail |
fail:ReceptionFailure
|
|
| Packaging Failure (inc. mismatched Content-Type) | Fail |
fail:PackagingFailure
|
|
| Malformed Response Message, e.g. malformed XML, message contains a DTD, invalid SOAP Envelope | Fail |
fail:BadResponseMessage
|
|
7.4.2 Behaviour of Responding SOAP Node
The overall flow of the behaviour of a Requesting SOAP Node follows the outline state machine description contained in 6.2 Single-Request-Response MEP. The following subsections describe each state in detail.
7.4.2.1 Init
| Statename | Receiving | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Waiting for the start of an inbound Request Message | ||
| Preconditions | Reception of an HTTP POST request at an HTTP endpoint bound to the local SOAP Node, see 6.2.3 Formal Description. | ||
| Postconditions | See below | ||
| Transitions | Event/Condition | NextState | Action |
| Receive the beginning of an HTTP POST Request containing well formed Request Message. | Receiving |
This change of state represents a transfer of control of the inbound message exchange context to the local SOAP node. |
|
| Receive HTTP POST Request containing malformed Request Message | Fail |
The message is deemed to have been intended for the local SOAP node, but is deemed badly formed: ill-formed XML, contains a serialized DTD, and/or does contain an invalid SOAP envelope. The local SOAP node generates SOAP fault message in accordance with the table below which it sends in the corresponding HTTP response message, accompanied by a status code value appropriate to the particular fault. The message exchange context may be destroyed or considered not to have been created. |
|
| Problem with Message | HTTP Status Code | HTTP reason phrase (informative) | SOAP fault |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ill-formed XML or invalid SOAP Envelope (of this SOAP Version) | 400 | Bad request | None |
| Unsupported message encapsulation method | 415 | Unsupported Media | None |
7.4.2.2 Receiving
| Statename | Receiving | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Continue Receiving the Request Message and wait for the start of a Response Message to be available in the Message Exchange Context. | ||
| Preconditions | None | ||
| Postconditions | See below | ||
| Transitions | Event/Condition | NextState | Action or Failure Reason |
The start of an abstraction of a Response Message becomes available in context:OutBoundMessage indicating that the local SOAP has generating a Response Message.
|
Receiving+ Sending |
context:OutboundMessage MAY contain a SOAP fault.
Formulate and start sending the Response Message (see table below) |
|
| Underlying protocol error | Fail |
fail:transmissionFailure
|
|
| Local abort | Fail |
fail:localAbort Abort HTTP operation (??)
|
|
| Header | Value |
|---|---|
| Status line | Set according to the following table |
| Content-Type | "application/soap+xml" (see 7.1 Introduction) |
| Additional Headers | Generated in accordance with the rules for the binding specific expression of any optional features in use for this message exchange e.g. SOAPAction (see 7.5.1 SOAP Action). |
| HTTP entity body |
XML 1.0 serialisation of the SOAP message XML Infoset carried in the context:OutboundMessage property of the message exchange context. This binding mandates support
for UTF-8 and UTF-16.
|
| SOAP fault | HTTP status code | HTTP reason phrase (informative) |
|---|---|---|
| Non-fault Response Message | 200 | OK |
| env:VersionMismatch | ?? | |
| env:MustUnderstand | ?? | |
| env:DataEncodingUnknown | ?? | |
| env:Sender | ?? | |
| env:Receiver | ?? | |
| env:rpc | ?? | |
| Other faults | ?? |
7.4.2.3 Receiving+Sending
| Statename | Responding | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Completing Request Message reception and Response Message transmission. | ||
| Preconditions | None | ||
| Postconditions | See below | ||
| Transitions | Event/Condition | NextState | Action or Failure Reason |
| Response Message Reception completed and Request Message Transmission | Success | ||
| Underlying protocol error | Fail |
fail:TransmissionFailure .
|
|
| Local abort | Fail |
fail:localAbort Abort HTTP operation (??)
|
|
7.4.2.4 Success and Fail
These are the terminal states for a given instance of a single-request-response message exchange. From the point-of-view of the local node this message exchange has completed.
7.5 Features Expressed External to the Message Envelope
This underlying protocol binding specification defines a binding specific expression for the following features:
-
"http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/bindings/HTTP/SOAPAction/"
Other features that are compatible with the message exchange patterns listed above are supported using their generic in-envelope expression defined in the relevant feature specification.
7.5.1 SOAP Action
This sub-section defines a binding specific optional feature named:
-
"http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/binding/HTTP/SOAPAction/"
In the text to follow, the prefix "action" is mapped to the URI "http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap/binding/HTTP/SOAPAction/"
Some SOAP Receivers using this binding might need certain information to be readily available outside the message envelope. This binding uses an externalised expression of the SOAP Action feature to supply this information.
Use of the SOAP Action feature is OPTIONAL. SOAP Receivers MAY use it as a hint to optimise processing, but SHOULD NOT require its presence in order to operate. Support for SOAPAction is OPTIONAL in implementations. Implementations SHOULD NOT generate or require SOAPAction UNLESS they have a particular purpose for doing so (e.g., a SOAP Receiver specifies its use).
| Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
action:SOAPActionURI
|
Used to hold the SOAPAction feature value.
The type of this property is anyURI in the namespace named "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-datatypes". Relative URIs are interpreted relative to the Request-URI. |
action:RequiredSOAPActionURI
|
If a SOAP Receiver does require the action:SOAPActionURI property in order to operate, it MAY respond to requests which either convey an unrecognised
action:SOAPActionURI value or convey no action:SOAPActionURI value with a response containing an action:RequiredSOAPActionURI property. The SOAP
Receiver SHOULD ensure that an HTTP status code of 427 (SOAPAction required) is returned to the corresponding HTTP client.
The type of this property is anyURI in the namespace named "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-datatypes". Relative URIs are interpreted relative to the Request-URI. |
The action:SOAPActionURI and action:RequiredSOAPActionURI properties are represented in HTTP using the HTTP headers SOAPAction and Required-SOAPAction
respectively. The following table shows the points at which the property values and HTTP header values are exchanged.
| Property Name | Request | Response |
|---|---|---|
action:SOAPActionURI
|
If action:SOAPActionURI property is present in the message exchange context, its value is sent as the value of a SOAPAction HTTP header
|
N/A |
action:RequiredSOAPActionURI
|
N/A |
If a Required-SOAPAction HTTP header is present, its value is inserted into the message exchange context as the value of the action:RequiredSOAPActionURI property.
|
| Property Name | Request | Response |
|---|---|---|
action:SOAPActionURI
|
If a SOAPAction HTTP header is present, its value is inserted into the message exchange context as the value of the action:SOAPActionURI property.
|
N/A |
action:RequiredSOAPActionURI
|
N/A |
If an action:RequiredSOAPActionURI property is present in the message exchange context, its value is sent as the value of a Required-SOAPAction HTTP
header
|
The syntax for the SOAPAction and Required-SOAPAction HTTP headers fields is defined as follows:
SOAP Action HTTP Header
| [4] |
soapaction
|
::= |
"SOAPAction" ":" <"> URI-reference <">
|
| [5] |
URI-reference
|
::= |
<as defined in RFC2396>
|
Required SOAP Action HTTP Header
| [6] |
req-soapaction
|
::= |
"required-SOAPAction" ":" <"> URI-reference <">
|
7.6 Security Considerations
The SOAP HTTP Binding (see 7. SOAP HTTP Binding) can be considered as an extension of the HTTP application protocol. As such, all of the security considerations identified and described in section 15 of the HTTP specification[2] apply to the SOAP HTTP Binding in addition to those described in Part 1 [SOAP-PART1] "Security Considerations". Implementers of the SOAP HTTP Binding should carefully review this material.