- From: Savas Parastatidis <Savas.Parastatidis@newcastle.ac.uk>
- Date: Thu, 2 Dec 2004 09:50:02 -0000
- To: "Francisco Curbera" <curbera@us.ibm.com>, <public-ws-addressing@w3.org>
- Message-ID: <37E80E80B681A24B8F768D607373CA8001854BD8@largo.campus.ncl.ac.uk>
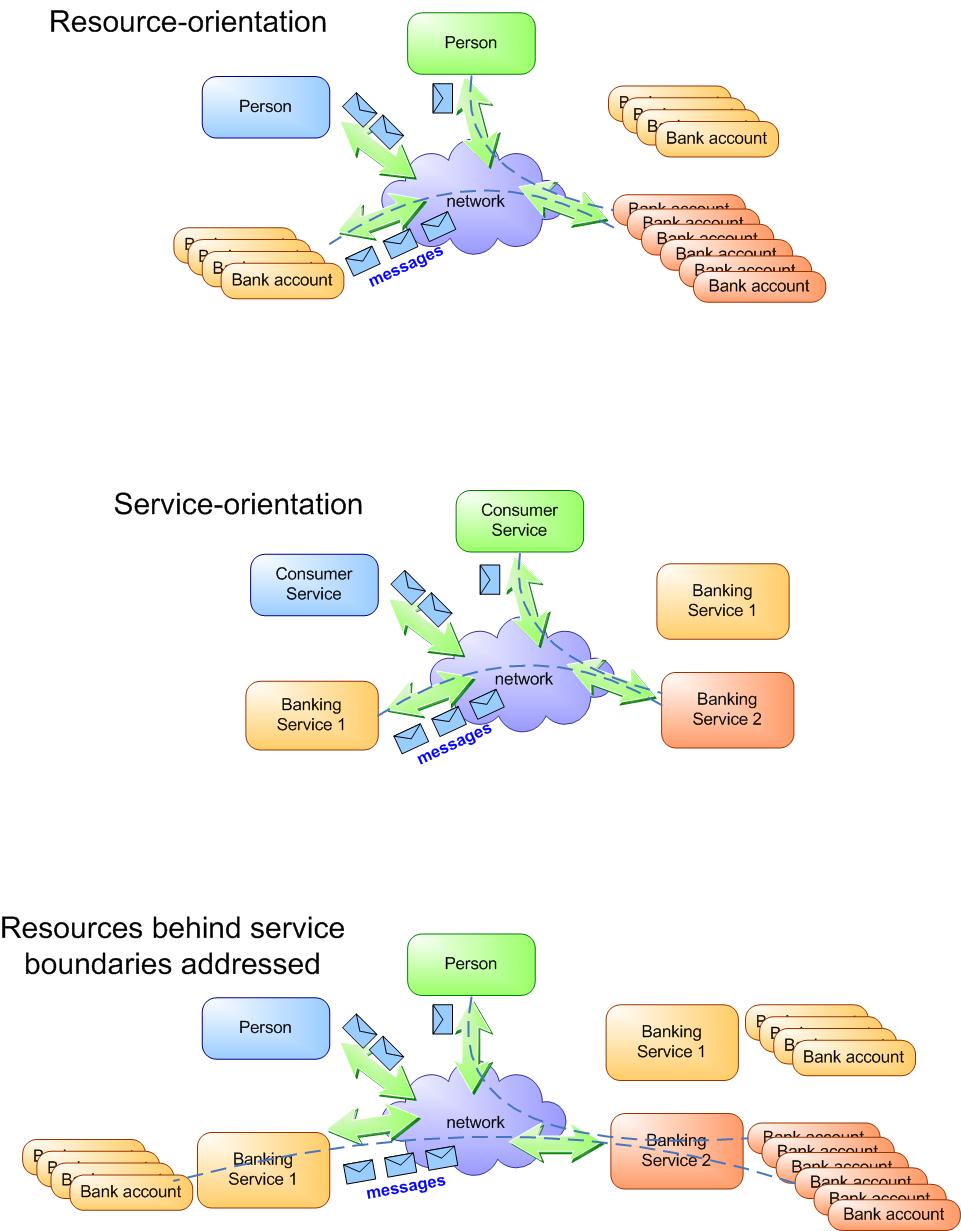
Dear Paco, As I mentioned in another message I agree with your view that EPRs are not identifiers. So, it's not surprise that I also agree with your analysis and proposed editorial changes. However, I would like to make the following comments... For a specification called Web Services Addressing I find it surprising that your analysis does not include the term "service" (except in the quotes taken from the spec). I see this as an architectural-related issue that is an important one and that relates to the way we see the entities we want to address. So, do we see the architecture consisting of a set of resources (our architectural elements) that exchange messages or as a set of services that exchange messages or, perhaps, both? 1. A resource-oriented architecture The addressable units are the resources. Resources communicate with each other by exchanging messages. This is a similar approach to the Web and some would argue like traditional object-based approaches (e.g. CORBA/DCOM). There is no need for an explicit actor, the "service". We reason in terms of resources only. 2. A service-oriented architecture The addressable units are the services. Services communicate with each other through the exchange of messages. The messages may carry additional information to allow them to reason about stateful interactions (in the form of WS-Context, RefProps/RefParams, WS-AtomicTransaction, Ws-SecureConversation, etc.). However, the addressable units are still the services themselves. Actors in the architecture don't have any other architectural element to reason about. It's just services. 3. A mix of the above two. In this case both services and resources can be addressed. This is the model that WS-RF seems to follow. Is this the model you have in mind? I was wondering whether others had a similar view to mine as to whether resources residing behind the service boundaries should be explicitly addressable or not. I am not suggesting here that information should not be included in the EPR in the form of RefProps/RefParams (that's a different discussion) but I question whether resources should be explicitly addressed as far as actors in the architecture are concerned. Put another way... As someone who uses an EPR, do I know that I address my message to a resource or a service? The above three could be summarised with an example (also refer to attached figure). As a user of an EPR: - Do I know that I talk to my "bank account" _directly_ (in which case we don't need the service/actors)? The "bank account" is what Paco refers to as the "stateful resource" which is now explicitly addressed. - Do I know that I talk to a "banking service" _about_ my bank account, which is explicitly identified in my interactions? My interaction has to explicitly identify the bank account as part of the semantics of the message exchange (the identity is not hidden inside an opaque EPR). - Do I know that I talk to my "bank account" _through_ a "banking service", which means that a back-end (logical or representation of a) resource is explicitly addressed? Now I know that I talk to a stateful resource without knowing its identity (perhaps there was a previous association between the identity and the EPR). I am aware that some may not see a difference between a resource and a service. However, my understanding is that W3C sees as a resource anything identified using a URI (I hope the experts in this group will correct me). Since the analysis bellow, with which I agree, suggests that EPRs are not used as identifiers, and since I as a user am not allowed to reason about the identity of a resource included in RefProps/RefParams (opaqueness of EPRs), it's suggested to me that services and resources are treated differently for addressing purposes in some cases (e.g. WS-RF and WS-Transfer). Is it valuable for this group for a distinction to be made? What do others think? Am I seeing a difference that doesn't really exist? Best regards, -- Savas Parastatidis http://savas.parastatidis.name > -----Original Message----- > From: public-ws-addressing-request@w3.org [mailto:public-ws-addressing- > request@w3.org] On Behalf Of Francisco Curbera > Sent: 01 December 2004 18:00 > To: public-ws-addressing@w3.org > Subject: i0001: EPRs as identifiers - alternative proposal > > > Following up on my action Item from last week, here is my proposal for how > to deal with issue 1- and why. > > Rationale > ======= > > EPRs are not identifiers, only addresses. Let me explain. > > What is required from an identifier? > ------------------------------------------ > > An identifier to be useful must allow meaningful comparison for identity > or > "sameness". This requires them to overall unique and unambiguous, > otherwise > no meaningful comparison is possible. Moreover one could argue that to be > really useful identifiers should not be reused once they've been made > invalid. > > Are EPRs identifiers? > -------------------------- > > No, in view of the above and the use cases EPRs are intended to support. > > First, multiple EPRs may be issued for accessing the same resource. This > is > the case when multiple protocols are available to access a resource (note > that allowing multiprotocol EPRs does not imply that every EPR is > multiprotocol, so single protocol EPRs must be assumed to exist even in > multiprotocol environments). When considering long living stateful > resources this is particularly clear: resources may move and EPRs may > become stale and need to be refreshed while accessing the same stateful > resource. No meaningful comparison can be carried out in these cases. > > Also, the spec clearly states the opaqueness principle: only the issuer > understands the actual runtime meaning of the EPR contents (stuff other > than metadata). This is so to allow the server the side to freely manage > those EPRs, generating aliases if required or virtualizing the meaning of > EPRs. This freedom is fundamental for effectively managing resources, but > is incompatible with the notion that the EPR identifies the resource. > > Finally, looking at the information inside an EPRs and to the actual usage > of that information (as specified by the spec itself) it is clear that > there is not indication of identifier related operational semantics in the > spec: none of the two operations on EPRs that the spec recognizes > (comparison and serialization) are compatible with identifier semantics > but > with those of addresses (more below). The language used in certain > paragraphs is another matter, and that is what I am proposing that we fix. > > So what are EPRs then? > ----------------------------- > > EPRs are a particular form of an address, XML based and with specific > operational semantics attached to it. EPRs encapsulate in XML the > information that a message needs to carry so it can reach the destination. > It is associated with specific operational semantics that state how that > information needs to be used to ensure that a message is delivered to the > right address. I think everyone will agree that this is the core meaning > of > an EPR. > > Note that there are no equivalent semantics to explain how they can be > used > as identities. The EPR comparison rules in Section 2.3 clearly disallow > any > conclusion regarding the identity of the resource being addressed. In > fact, > the only conclusion that it allows is completely consistent with the > address interpretation, since they exclusively refer to endpoint metadata, > i.e. what a requester needs to do to successfully send a message to the > endpoint. > > Discussion > ========= > > >From the arguments above I conclude that the text in certain paragraphs > of > the specification is inconsistent with its actual semantics. This is the > reason that has lead many people (and issue 1 as well) to mis-characterize > of EPRs as identifiers. This should be fixed by clarifying the text. > > One remaining question is whether EPR (as addresses) should be URIs but I > think this should be opened as a separate issue. The question I guess is > whether we believe them to be "Web addresses". For me the answer is > clearly > no, in the same way as other methods of addressing are not considered to > be > necessarily Web addresses, for example the use of URLs with HTTP cookies. > This however, is a different debate (issue) that we should have once issue > 1 is clarified with respect to the identity problem. > > > Proposed resolution > =============== > > Editorial changes to be introduced in the core specification to eliminate > any implication that EPRs identify resources. In particular replace > "identify" by "address" as appropriate in the following sections: > > Abstract: > ----------- > "to identify Web service endpoints and to secure end-to-end identification > of endpoints in messages." -> "to address Web service endpoints and to > secure end-to-end delivery of messages to endpoints." > > Section 1: > ------------ > (2nd para): "Endpoint references convey the information needed to > identify/reference a Web service endpoint" -> "Endpoint references convey > the information needed to address messages to a Web service endpoint". > > Section 2: > ------------ > (2nd bullet): "Identification and description of specific service > instances that are created as the result of stateful interactions." -> > "Addressing and description of specific service instances that are created > as the result of stateful interactions." > > Section 2.1: > -------------- > [address] property (even the use of "identify" is ambiguous here) "An > address URI that identifies the endpoint. This may be a network address or > a logical address." -> "A network or a logical URI address for the > endpoint". > [ref. props]: "identify" -> "address", remove additional "identification". > > Section 2.2: > -------------- > /wsa:EndpointReference/wsa:Address: change accoding to Section 2.2. > > Section 3: > ----------- > "identification and location" -> "addressing" > [reply endpoint], [fault endpoint]: "endpoint reference that identifies > the > intended receiver" -> "an endpoint reference for the intended receiver". > > > > >
Attachments
- image/jpeg attachment: Resource-_vs_Service-_vs_Service-Resource-orientation.jpg
Received on Thursday, 2 December 2004 09:51:32 UTC